Anemia
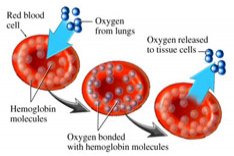
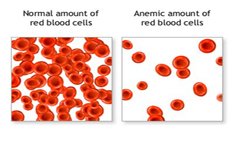
Anemia is a condition where the red blood cells of a person drop below normal. In a blood test, this is generally measured as a hemoglobin level Jbelow 12 grams per 100 ml blood or a hematocrit Level below 40%. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin that is responsible for carrying oxygen to all the cells of the body. Thus, anemia can cause lack of oxygen in various cells leading to health problems, including fatigue and stress on bodily organs. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a substance that picks up oxygen from lungs, carries it throughout body, and gives it to cells. Cells need oxygen to perform the basic functions that generate energy and keep us alive.
According to WHO estimates, India is one of the countries in the world that has highest prevalence of anemia. NFHS shows a disturbing presence of anemia in pregnant and lactating women. The disease troubles 59% cases of pregnancy while 63 % of lactating women are anemic. States like Bihar and Rajasthan register 60 per cent of pregnant women to be anemic, 10 per cent growth of anemic pregnancy in these states is pretty alarming.
Causes of Anemia
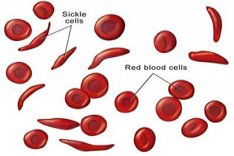
Anemia can be caused by many things, like excessive destruction of RBCs, blood loss or inadequate production of RBCs. All conditions causing anemia usually work through one of these mechanisms. Causes include nutritional deficiencies (most notably iron or vitamin deficiencies), inherited disorders (such as Thalassemia or’Sickle Cell anemia), infections, some kinds of cancer, exposure to certain medicines or chemicals, autoimmune hemolysis (where the red blood cells are destroyed by a dysfunction in the body’s own immune system), excessive bleeding, etc.
In India, the commonest cause of anemia is iron deficiency. Iron deficiency is frequently blamed on poor nutrition as Indian diet is generally low in iron. Growing children, menstruating women, pregnant women and strict vegetarians are more susceptible to iron deficiency. Vegetarian diet generally has less absorbable iron.
Symptoms of Anemia
Most people do not experience many symptoms even when hemoglobin drops below 12 grams, until it drops to less than 10 grams or so. Early symptoms could include light-headedness, fatigue, shortness of breath and inability to perform some activities that they could previously do. In cases where the hemoglobin drops to 7 grams or less, people may have difficulty performing activities of their daily living. For instance, there may be difficulty moving around the house, putting on clothes, cooking, or even taking bath. Anemia starts affecting the cardiac muscles, as the heart starts doing more work trying to compensate for the depleted oxygen supply to the cells.
In cases where the hemoglobin is less than 4 grams, people may become prostrate unable to perform any significant activity. There is the grave risk of heart failure and even death. However, it must be noted that symptoms depend not only on the absolute level of hemoglobin, but also on the patient’s general condition. Also, if anemia develops more slowly the body adjusts and may not experience typical symptoms. Symptoms also depend on the cause of anemia.
When do blood transfusions become necessary?
Blood transfusion is generally not recommended, unless the hemoglobin drops below 7 grams and significant symptoms even at a higher level. Clinical studies have shown that the heart starts getting affected significantly at about this Level. So, 7 has been determined as the crirical level at which blood transfusion is considered, no matter what the etiology is.
To prevent anemia, one need to eat a diet that is rich in iron, B12, folic acid and other nutrients. For non vegetarian the richest foods in, iron, B12 and folic acid are seafood, liver anoft. marrow soup. For vegetarians, good options are milk products, Lentils (ex: bajra), spinach, methi, cabbage, cauliflower, sweet potatoes, prunes and green leafy vegetables, legumes, beans, nuts, dry fruits like raisins, apricot, khajur.
Green leafy vegetables are rich in iron, but most of the iron is not available to the body as the greens have chemicals that bind and do not release the iron. So, the body gets to absorb only a fraction of the iron present in greens. After food, drinking or eating something with vitamin C in it, such as lemonade, tomato juice or oranges, significantly increases iron absorption as well as being healthy in and of itself.