Blood Components
What’s Your Type ?
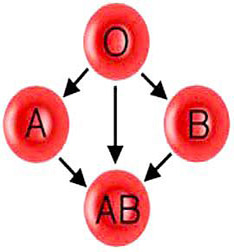
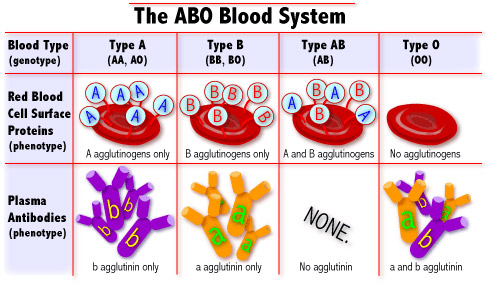
In some ways, every person’s blood is the same. But, when analyzed under a microscope, distinct differences are visible. In the early 20th century, an Austrian scientist named Karl Land Steiner classified blood according to those differences. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for his achievements. Land Steiner observed two distinct chemical molecules present on the surface of the red blood cells. He labeled one molecule “A” and the other molecule “B” If the red blood cells had only “A” molecules on it, that blood was called type A. If the red blood cells had only “B” molecules on it, that blood was called type B. If the red blood cells had a mixture of both molecules, that blood was called type AB. If the red blood cells had neither molecule, that blood was called type.
If two different blood types are mixed together, the blood cells may begin to clump together in the blood vessels, causing a potentially fatal situation. Therefore, it is important that blood types be matched before blood transfusion take place. In an emergency, type O blood can be given because it most likely to be accepted by all blood types. However, there is still a risk involved.
A person with type A blood can donate blood to a person with A or type AB. A person with type B blood can donate blood to a person with type B or type AB. A person with type AB blood can donate blood to a person with type AB only. A person with type O blood can donate to anyone.
A person with type A blood can receive blood from a person with type A or type 0. A person with type B blood can receive blood from a person with type B or type O. A person with type AB blood can receive blood from anyone. A person with 0 blood can receive blood from a person with type O only.
Because of these patterns, a person with type O blood is said to be a universal donor. A person with type AB blood is said to be universal receiver. In general, however, it is still best to mix blood of matching types and Rh Factors.
Life Blood
The average adult has about five liters of blood living inside of their body, coursing through their vessels, delivering essential elements and removing harmful wastes. Without blood, the human body would stop working.
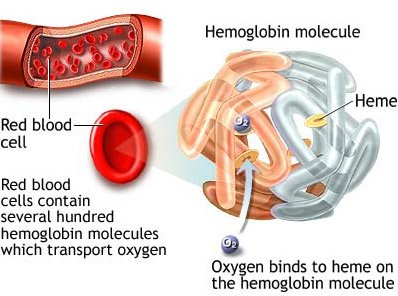
Blood is the fluid of life, transporting oxygen from the lungs to body tissue and carbon dioxide from body tissue to the lungs. Blood is the fluid of growth, transporting nourishment from digestion and hormones from glands throughout the body. Blood is the fluid of health, transporting disease fighting substances to the tissue and waste to the kidneys.
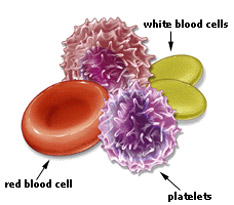
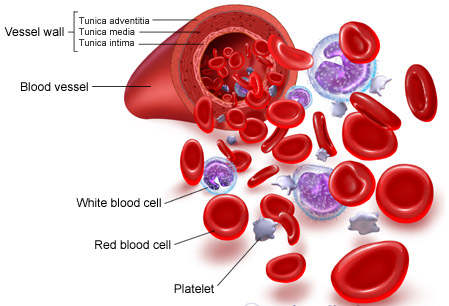
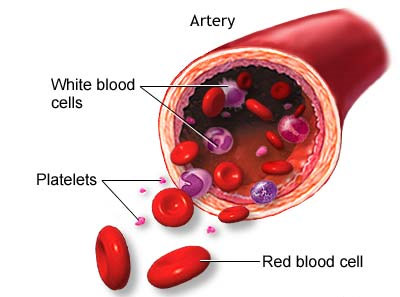
Because it contains living cells, blood is alive. Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells are responsible for nourishing and cleansing the body. Since the cells are alive, they too need nourishment. Vitamins and Minerals keep the blood healthy. The blood cells have a definite life cycle, just as all living organisms do.
Approximately 55 percent of blood is Plasma, a straw-colored clear liquid. The liquid plasma carries the solid cells and the Platelets which help blood clot Without blood platelets, you would bleed to death.
When the human body loses a little bit of blood through a minor wound, the platelets cause the blood to clot so that the bleeding stops. Because new blood is always being made inside of your bones, the body can replace the lost blood. When the human body loses a lot of blood through a major wound, the blood has to be replace through a blood transfusion from other people.
But everybody’s blood is not the same. There are four different Blood Types. Plus your blood has Rh Factors which make it even more unique. Blood received through a transfusion must match your own Patients who are scheduled to have major surgery make Autologous Blood Donations (donations of their own blood) so that they have a perfect match.
Blood Groups, Blood Typing and Blood Transfusions The discovery of blood groups Experiments with blood transfusions, the transfer of blood or blood components into a person’s blood stream, have been carried out for hundreds of years. Many patients have died and it was not until 1901, when the Austrian Karl Landsteiner discovered human blood groups, that blood transfusions became safer.
Mixing blood from two individuals can lead to blood clumping or agglutination. The clumped red cells can crack and cause toxic reactions. This can have fatal consequences. Karl Landsteiner discovered that blood clumping was an immunological reaction which occurs when the receiver of a blood transfusion has antibodies against the donor blood cells.
Karl Landsteiner’s work made it possible to determine blood groups and thus paved the way for blood transfusions to be carried out safely. For this discovery he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930.
What is blood made up of?
An adult human has about 4–6 liters of blood circulating in the body. Among other things, blood transports oxygen to various parts of the body.
Blood consists of several types of cells floating around in a fluid called plasma. The red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen. Red blood cells transport oxygen to, and remove carbon dioxide from, the body tissues. The white blood cells fight infection. The platelets help the blood to clot, if you get a wound for example. The plasma contains salts and various kinds of proteins.
What are the different blood groups?
The differences in human blood are due to the presence or absence of certain protein molecules called antigens and antibodies. The antigens are located on the surface of the red blood cells and the antibodies are in the blood plasma. Individuals have different types and combinations of these molecules. The blood group you belong to depends on what you have inherited from your parents.
There are more than 20 genetically determined blood group systems known today, but the AB0 and Rh systems are the most important ones used for blood transfusions. Not all blood groups are compatible with each other. Mixing incompatible blood groups leads to blood clumping or agglutination, which is dangerous for individuals.
Nobel Laureate Karl Landsteiner was involved in the discovery of both the AB0 and Rh blood groups
| AB0 blood grouping system : | According to the AB0 blood group system there are four different kinds of blood groups: A, B, AB or 0 (null). |
| Blood group A : | If you belong to the blood group A, you have A antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and B antibodies in your blood plasma. |
| Blood group B : | If you belong to the blood group B, you have B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and A antibodies in your blood plasma. |
| Blood group AB : | If you belong to the blood group AB, you have both A and B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and no A or B antibodies at all in your blood plasma. |
| Blood group 0 : | If you belong to the blood group 0 (null), you have neither A or B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells but you have both A and B antibodies in your blood plasma. |
| Rh factor blood grouping system : | Many people also have a so called Rh factor on the red blood cell’s surface. This is also an antigen and those who have it are called Rh+. Those who haven’t are called Rh-. A person with Rh- blood does not have Rh antibodies naturally in the blood plasma (as one can have A or B antibodies, for instance). But a person with Rh- blood can develop Rh antibodies in the blood plasma if he or she receives blood from a person with Rh+ blood, whose Rh antigens can trigger the production of Rh antibodies. A person with Rh+ blood can receive blood from a person with Rh- blood without any problems. |
Blood Component Preparation 2009
| Month | RCC | FFP | PRC | PRP |
| January | 281 | 281 | 84 | 0 |
| February | 206 | 206 | 70 | 0 |
| March | 274 | 274 | 87 | 0 |
| April | 306 | 306 | 111 | 0 |
| May | 187 | 187 | 80 | 0 |
| June | 211 | 211 | 85 | 0 |
| July | 188 | 188 | 88 | 0 |
| August | 131 | 131 | 97 | 0 |
| September | 184 | 184 | 184 | 0 |
| October | 179 | 179 | 131 | 0 |
| November | 0 | |||
| December | 0 | |||
| Total | 2147 | 2147 | 1017 | 0 |